|
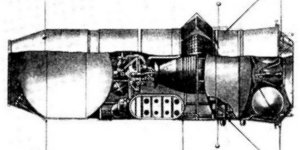
The 7K Soyuz spacecraft was initially designed for rendezvous and docking operations in near earth orbit, leading to piloted circumlunar flight. A circumlunar mission would begin with launch of the Soyuz B 9K rocket block into a 225 km orbit. This would be followed by one to three Soyuz V 11K tankers (depending on the mission), which would automatically rendezvous and dock with the 9K. They would transfer up to 22 metric tons of propellant. Finally the Soyuz A 7K spacecraft with the cosmonauts aboard would be launched, dock with the 9K, and be propelled on a lunar flyby trajectory.
Although Vladimir Chelomej's plan for a single, manned spacecraft, to be placed on a translunar trajectory in a single launch of his UR-500K rocket, was the preferred approach, Sergej Korolyov continued work on the Soyuz A 7K design, which evolved into the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft.
References:
Encyclopedia Astronautica.
Russian Space Web.
Wikipedia.
|